Table of Contents
ToggleFrom flow control to directional control pneumatic valves, each type brings different crucial advantages because of their unique designs.
They have various different operators, materials, and much more to choose from, so understanding each type of it will be beneficial for helping industries make an informed choice.
This article is intended to help you gain insight into the numerous types of pneumatic valves, including their materials and applications.
What is Pneumatic and How Do They Work?
Pneumatic refers to a system that uses compressed air or gas to generate power and make the other components work. As a result, they’re safe, light weight, and able to have rapid movements, which is perfect for different industrial uses too.
Their key components are compressors, storage tanks, actuators, hoses, and valves. These contribute to compressing air gathered from the atmosphere, while the valves transport it to the actuators to generate mechanical energy.
Common Types for Pneumatic Valves
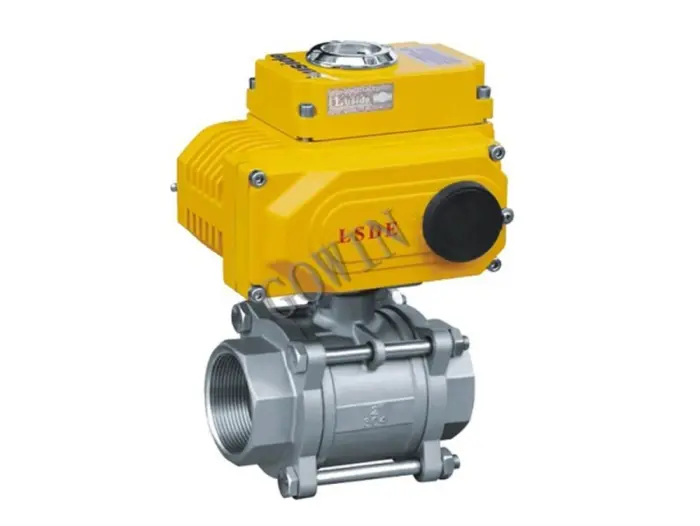

Pneumatic Ball Valve
A round ball is the sealing component of this pneumatic type, which turns to control the passage of air to the actuator. When the hole is aligned in the path, the valve is open. However, when the solid part is facing the passage when the valve is closed.
Therefore, the simple design makes it perfect for uses that require quick on and off operations. Although they can be more expensive than normal ball valves, they’re worth an investment because they’re faster than electric-actuated.
Pneumatic Control Valve
This pneumatic valve has a feedback mechanism. This enables it to specifically adjust the valve’s stem according to the desired air pressure and flow according to the controller’s commands.
This makes these types of valve energy sufficient for operations because they ensure they supply the right amount of compressed air to the system.
Pneumatic Directional Valve
They’re also called spool valves. This can have several air pathways, from 2 to 5 openings. This allows it to deliver compressed air to different actuators or cylinders in the system at once. As a result, this pneumatic directional valve is perfect for complex and large systems.
Pneumatic Operated Butterfly Valve
This type of pneumatic valve regulates the flow of medium via a disk that spins with compressed air pressure. This occurs when the compressed air enters the actuator and exerts pressure on the diaphragm, causing the disc 90 degrees to completely open or close the valve.
Furthermore, these pneumatic valves take less space while they offer excellent quick on and off operations.
Types of Pneumatic Valves Operators
Air Operated
This is a common operator for pneumatic valves. Most of these designs used compressed air or gas to push the diaphragm and the actuator stem in order to close the valve.
As a result, the sealing component that is attached to the mentioned components is also pressed against the seat. The valve will only open if the air leaves the diaphragm.
Solenoid Operated
A pneumatic valve that is solenoid operated uses electricity for managing the flow of air or gas in a system.
When an electric current is applied to the solenoid coil, it moves the plunger. This enables the valve ports to open and close, allowing or blocking the compressed air from its openings to the corresponding cylinder port.
Thus, the valve will open if the compressed air enters the cylinder’s extended port. However, it will close the valve when the solenoid coil is de-energized and the air is delivered into the cylinder’s retract port.
If you want to learn more about this type of operator, this informational video may assist you.
Mechanical or Manually Operated
Pneumatic valves with these operators required human assistance in order to control the compressed air flow in the system. It doesn’t close or open the valve through electric or air, but it should be managed by the operator in a variety of ways, including:
- Lever
- Pull Rod
- Foot Pedal
- Push-Pull Button
Pneumatic Valve’s Different Materials
Pneumatic valves can also differ from each other in their materials, which gives them certain advantages. During material selection for your pneumatic valves, you had to consider the specific requirements you need, such as corrosion resistance.
Here are some of the materials to choose from:
| Materials’ name | Special Traits |
| Stainless Steel | Highly durable and resistant to corrosion because it has chromium. Thus, stainless steel, particularly grades 316 and 304, makes it ideal for environments containing chemicals in the air. |
| Brass | More affordable, easy to manufacture, and has great corrosion resistance to the environment with fewer aggressive elements. |
| Monel | One of the nickel alloys that is excellent at high temperatures up to 900°F without breaking. |
Available Advanced Features for Pneumatic Valves
3D printed
3D printing or additive manufacturing allows the manufacture of complex pneumatic valve designs with minimal production time and waste.
Furthermore, it allows easy adjustment and customization of the pneumatic valve’s design due to the layer-by-layer construction process.
Its materials can be durable plastics like nylon and soft materials such as silicone rubber.
Smart Materials
Various valves began using smart materials for convenience of use in several fields. To illustrate, according to Annabell Efner et al., shape memory alloys (SMA) can also be used as actuators, including for pneumatic valves.
SMA’s shape memory effect refers to its ability to recover to its original shape after being deformed in cold temperatures. This showed that this specific alloy is also beneficial for pneumatic valves.
IoT-Enabled Valves
Some modern pneumatic valves like Festo’s VTEM, have integrated the Internet of Things (IoT) and often incorporated it with smart sensors, which allows industries to monitor and control the valve.
As a result, pneumatic valves with these features provide real information about the system’s performance, like its pressure, flow rates, and temperatures.
Gowin: Pneumatic Valve Manufacturer
Gowin’s long experience leads to becoming one of the prominent manufacturers for valves used in several kinds of industries, such as oil and gas, power plants, and much more.
They offer various products, including pneumatic valves, that conform to multiple international standards and guarantee high quality, such as:
Thus, don’t hesitate to contact Gowin for more information and get a quote now for your next pneumatic valves.
Pneumatic Valves: FAQ
How does a pneumatic air valve work?
Pneumatic air valves work by the compressor increasing the air’s pressure, allowing the actuator to open or close the valve using compressed medium as a mechanical force, either by pulling the sealing component away or against it.
What are the requirements for pneumatic pressure testing?
According to ASME B31.1 Power Piping Code, the pneumatic pressure testing should be between 1.2 and 1.5 times the designed maximum pressure of the system.
This is also applicable to the pneumatic valves to ensure safe operation during unexpectedly high pressures.
- Chemical Compatibility for 304 vs. 316 Stainless Steel
- A Design Approach for a Valve Based on a Magnetic Shape Memory Actuator
- Directional Control Valve Working Animation | 5/2 Solenoid Valve | Pneumatic Valve Symbols Explained
- How Pneumatic Control Valve Works | Control Valve Actuator Types | Control Valve Positioner Types
- Design and Characterization of a 3D-printed Pneumatically-driven Bistable Valve with Tunable Characteristics