Table of Contents
ToggleWhen choosing the right actuator for your industrial applications, understanding the difference between single-acting and double-acting actuators is crucial. These two actuator types play essential roles in controlling valves, and knowing their distinctions ensures optimal performance for your system.
What Is a Single Acting Actuator?
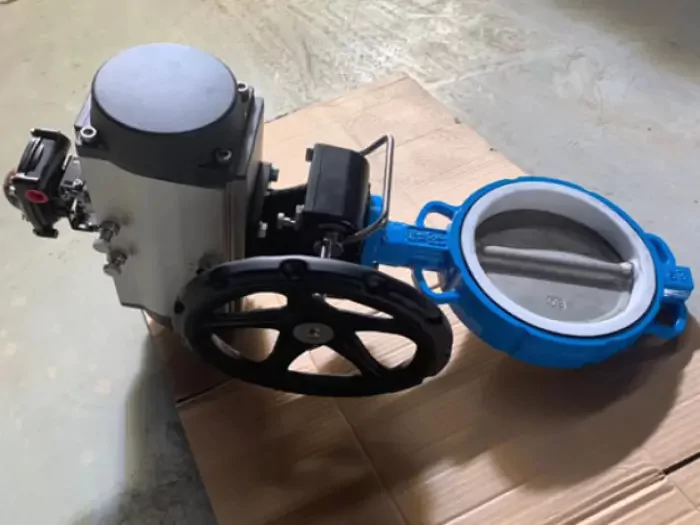
A single-acting actuator uses air or hydraulic pressure to move in one direction and relies on a spring to return to its original position. This design is simple and efficient, making it ideal for applications where fail-safe operation is a priority.
For example, in emergencies, the spring mechanism ensures the valve returns to its default state, whether open or closed. Single-acting actuators are known for:
- Fail-Safe Capability: Automatically returns to a safe position during power or pressure loss.
- Energy Efficiency: Consumes less air or hydraulic fluid since it operates in one direction only.
- Compact Design: Often smaller and lighter due to fewer internal components.
What Is a Double-Acting Actuator?
A double-acting actuator uses air or hydraulic pressure for both extending and retracting movements. Unlike single-acting actuators, it does not rely on a spring for return motion. Instead, pressure is applied alternately to either side of a piston to achieve precise control and force in both directions.
Double-acting actuators are known for:
- Precise Control: Provides consistent force and movement in both directions.
- Higher Torque Output: Delivers greater force, making it suitable for demanding applications.
- Durability: Designed for applications where frequent cycling is required.
Key Differences Between Single-Acting and Double-Acting
Understanding the differences between single-acting and double-acting actuators helps in selecting the right one for your needs. Here are the key distinctions:
Power Source
- Single-acting actuators use air or hydraulic pressure in one direction, relying on a spring for the return.
- Double-acting actuators use air or hydraulic pressure in both directions.
Fail-Safe Operation
- Single-acting actuators provide fail-safe capabilities, ensuring the valve returns to a safe position during a power loss.
- Double-acting actuators do not have a built-in fail-safe mechanism unless external components are added.
Energy Consumption
- Single-acting actuators are more energy-efficient since they use power in one direction only.
- Double-acting actuators consume more energy due to the need for constant pressure in both directions.
Application Suitability
- Single-acting actuators are ideal for safety-critical systems like emergency shutdown valves.
- Double-acting actuators excel in applications requiring high torque and precise control.
Cost and Maintenance
- Single-acting actuators are generally more cost-effective and require less maintenance.
- Double-acting actuators may have higher upfront and operational costs due to their complexity.
Choosing the Right Actuator
When deciding between a single-acting or double-acting actuator, consider these factors:
- Application Requirements: Assess whether fail-safe operation is necessary for your system.
- Force and Torque Needs: Determine the level of force or torque required for your valve operation.
- Energy Efficiency: Factor in energy consumption and its impact on your operating costs.
- Environment: Consider whether the system operates in hazardous or high-temperature conditions.
- Budget: Evaluate both initial costs and long-term maintenance expenses.
Common Applications
Single-acting and double-acting actuators are tailored for specific industrial needs. Understanding where each type excels ensures optimal system performance. Below are common applications for both types:
Single Acting Actuators:
- Emergency shutdown systems
- Fail-safe valve operations
- Low-frequency cycling applications
Double Acting Actuators:
- High-torque valves
- Frequent cycling systems
- Precise flow control in process industries
Difference Between Single-Acting and Double-Acting Actuators: Conclusion
Understanding the difference between single-acting and double-acting actuators is essential for selecting the right solution for your system.
Whether you need the reliability of a single-acting actuator or the power of a double-acting actuator, GOWIN Industrial Valve offers high-quality options to meet your needs. Visit GOWIN today or get in touch with us to find the perfect actuator for your application!
Actuator Valves: FAQs
Which actuator provides more torque?
Double-acting actuators provide higher torque due to their bi-directional pressure control.
Can single-acting actuators handle high-torque applications?
Single-acting actuators are generally not suited for high-torque applications; double-acting actuators are a better choice.
What is the cost difference between single-acting and double-acting actuators?
Single-acting actuators are typically more cost-effective due to their simpler design and lower energy consumption.
Can a double-acting actuator fail to close?
Yes, but only if it is equipped with external components like a fail-safe mechanism or spring-return assembly.